What is Kali Purple?
Kali Linux, the popular Debian-based Linux distribution designed for digital forensics and penetration testing, announced a new project named Kali Purple, a distro designed for defensive security.
On a high level, Kali Purple consists of:
Over 100 defensive tools, such as:
- Arkime full packet capture
- Cyberchef
- Elasticsearch SIEM
- GVM vulnerability scanner
- TheHive incident response platform
- Malcolm
- Suricata IDS
- Zeek IDS
- and of course all the usual Kali tools
ISOs:
- Kali Purple
- Malcolm - based on Kali
- Hedgehog - based on Kali
A defensive menu structure according to NIST CSF:
- Identify
- Protect
- Detect
- Respond
- Recover
A gorgeous wallpaper and theme A reference architecture for the ultimate SOC In-A-Box; perfect for:
- Learning
- Practicing SOC analysis and threat hunting
- Security control design and testing
- Blue / Red / Purple teaming exercises
- Kali spy vs. spy competitions ( bare knuckle Blue vs. Red )
Kali Autopilot - an attack script builder / framework for automated attacks Defensive tools documentations Wiki Kali Purple Hub for the community to share:
- Practice pcaps
- Kali Autopilot scripts for blue teaming exercises
Kali Purple Discord channels for community collaboration and fun
Installation
Initially, check the comprehensive installation instructions for Kali Purple on VMWare Workstation, which were provided by @JonGoodCyber
Setting-up Elastic Stack
In this article, I’ll walk you through the deployment of Elasticsearch SIEM (Security Information and Event Management) with Kibana on Kali Purple.
https://gitlab.com/kalilinux/kali-purple/documentation/-/blob/main/301_kali-purple/installation.txt
1. Install Dependencies
1
2
3
4
sudo apt-get install curl
curl -fsSL https://artifacts.elastic.co/GPG-KEY-elasticsearch | sudo gpg --dearmor -o /etc/apt/trusted.gpg.d/elastic-archive-keyring.gpg
echo "deb https://artifacts.elastic.co/packages/8.x/apt stable main" | sudo tee -a /etc/apt/sources.list.d/elastic-8.x.list
sudo bash -c "export HOSTNAME=kali-purple.kali.purple; apt-get install elasticsearch -y"
The default username is elastic. Additionally, ensure that you save the password, which can be found under Security AutoConfiguration Information. 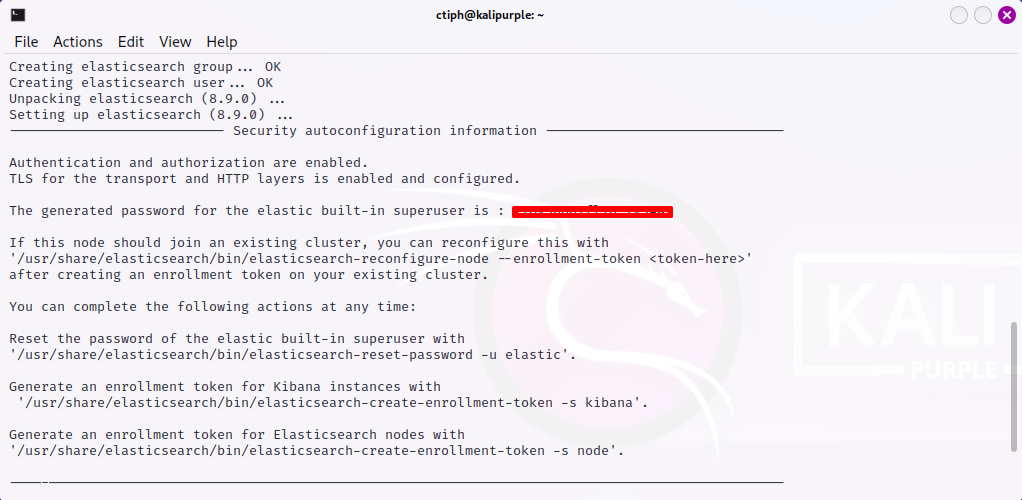
2. Convert to Single-Node Setup
1
2
sudo sed -e '/cluster.initial_master_nodes/ s/^#*/#/' -i /etc/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.yml
echo "discovery.type: single-node" | sudo tee -a /etc/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.yml
3. Install Kibana
1
2
sudo apt install kibana
sudo /usr/share/kibana/bin/kibana-encryption-keys generate -q
Add keys to /etc/kibana/kibana.yml
1
echo "server.host: \"kali-purple.kali.purple\"" | sudo tee -a /etc/kibana/kibana.yml
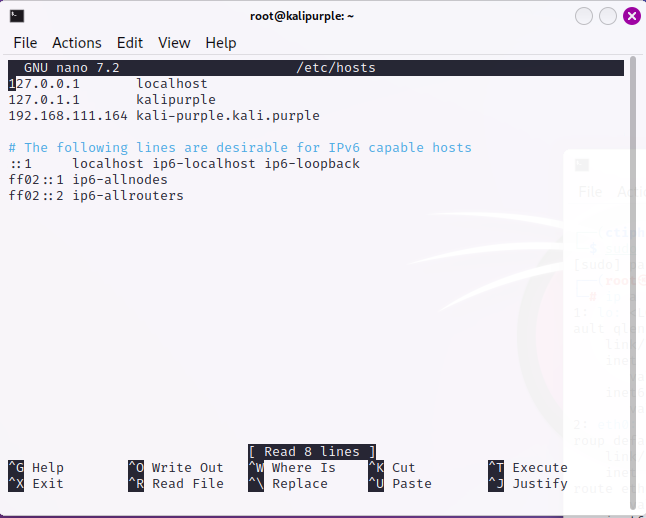
Ensure that kali-purple.kali.purple is only mapped to the IP address of your Kali Purple Machine in /etc/hosts in order to bind the Kibana interface.
Once done, you can now start Elasticsearch and Kibana.
1
sudo systemctl enable elasticsearch kibana --now
4. Enroll Kibana
To generate an Enrollment Token for Kibana, execute the following command in the terminal:
1
sudo /usr/share/elasticsearch/bin/elasticsearch-create-enrollment-token -s kibana
Next, open a web browser and navigate to the following address:
- http://{internal_ip_from_step_3}:5601
You will be redirected to the enrollment page of Kibana. At this point, paste the previously generated token.
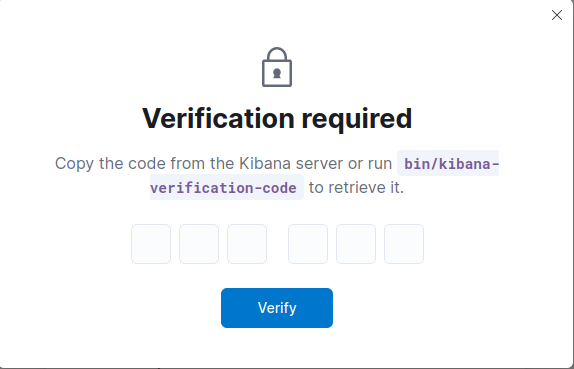
After that, you will be prompted to enter the Verification Code into Kibana.
To generate Verification Code for Kibana, execute the following command:
1
sudo /usr/share/kibana/bin/kibana-verification-code
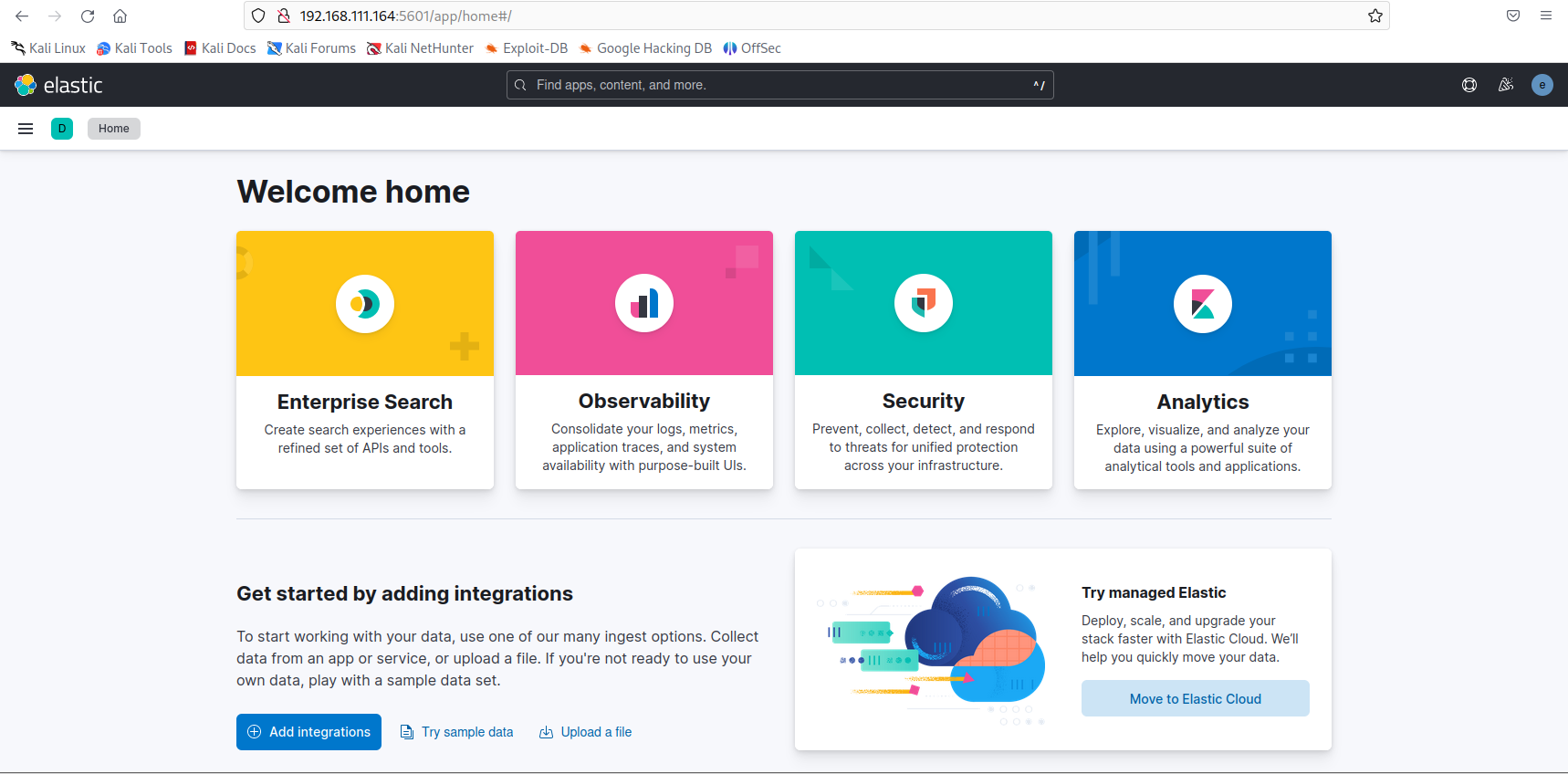
Then, enter the default username elastic along with the password generated in Step 1. Now, you can access Elasticsearch SIEM on Kali Purple.